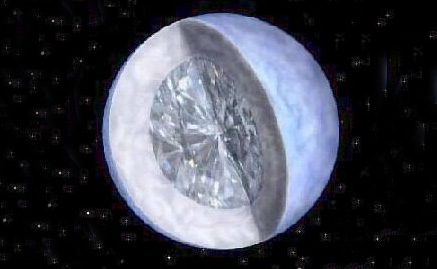
On Friday, 13th February, 2004, the Harvard-Smithsonian Centre for Astrophysics in Cambridge, Massachusetts, who study the origin, evolution and ultimate fate of the universe, released information about their latest discovery – a10 billion trillion trillion carat diamond.
The newly discovered cosmic diamond is a chunk of crystallized carbon, the size of our Moon, 50 light-years from the Earth in the constellation Centaurus. It is 4000kms wide and weighs 5 million trillion trillion pounds or 10 billion trillion trillion carats.
“You would need a jeweller’s loupe the size of the Sun to grade this diamond!” says astronomer Travis Metcalfe who leads the team of researchers that discovered the giant gem. The diamond has been called ‘Lucy’ – a tribute to the Beatles song ‘Lucy In The Sky With Diamonds’,
Technically known as BPM 37093, this huge cosmic gem, is actually a crystallized white dwarf. A white dwarf is the hot core of a star, left over after the star uses up its nuclear fuel and dies. It is made mostly of carbon and is coated by a thin layer of hydrogen and helium gases.
The white dwarf is not only radiant but also harmonious. It rings like a gigantic gong, undergoing constant pulsations. For more than four decades, astronomers have thought that the interiors of white dwarfs crystallized, but obtaining direct evidence became possible only recently. “The hunt for the crystal core of this white dwarf has been like the search for the Lost Dutchman’s Mine. It was thought to exist for decades, but only now has it been located,” says co-researcher Michael Montgomery.
The problem with proving the theory about the crystallization is that by the time the star has crystallized, it is no longer pulsating and is so cool, that they are impossible to detect. But BPM 37093 is so massive, that the star is crystallizing on the inside, as white light and sound continue to pulsate from the surface. The vibrations are detectable as colour shifts in the visible light emanating from the star. In this case, the right frequency makes it a diamond – blue green in tint.
“By measuring those pulsations, we were able to study the hidden interior of the white dwarf, just like seismograph measurements of earthquakes allow geologists to study the interior of the Earth. We figured out that the carbon interior of this white dwarf has solidified to form the galaxy’s largest diamond,” says Metcalfe.

Artwork by Lise Nilsen
Scientist Vince Ford, of the Australian National University’s Mount Stromio Observatory, said “This huge …..thing is sitting right down in the southern sky, in the constellation of Centaurus, just near the Southern Cross”. At approximately 4000kms in diameter, Lucy is roughly the same size as Australia and completely outclasses the largest diamond on Earth, the 530-carat Star of Africa that resides in the Crown Jewels of England. The Star of Africa was cut from the largest diamond ever found on Earth, a 3,100-carat gem.
Our Sun will also become a white dwarf when it dies 5 billion years from now. Some two billion years after that, the Sun’s ember core will crystallize as well, leaving a giant diamond in the centre of our solar system. The Sun is part of a group of stars called main sequence stars and most of these end their lives as white dwarves.
Sirius B, which is a known white Dwarf star, will also be a diamond in the future. Sirius B is currently around 25,000 degrees on the surface, and will begin to crystallize when it has cooled to about half that temperature.
References
Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics at:-
http://cfa-www.harvard.edu/press/pr0407.html
New Scientist at:
http://www.newscientist.com/news/news.jsp?id=ns99994692